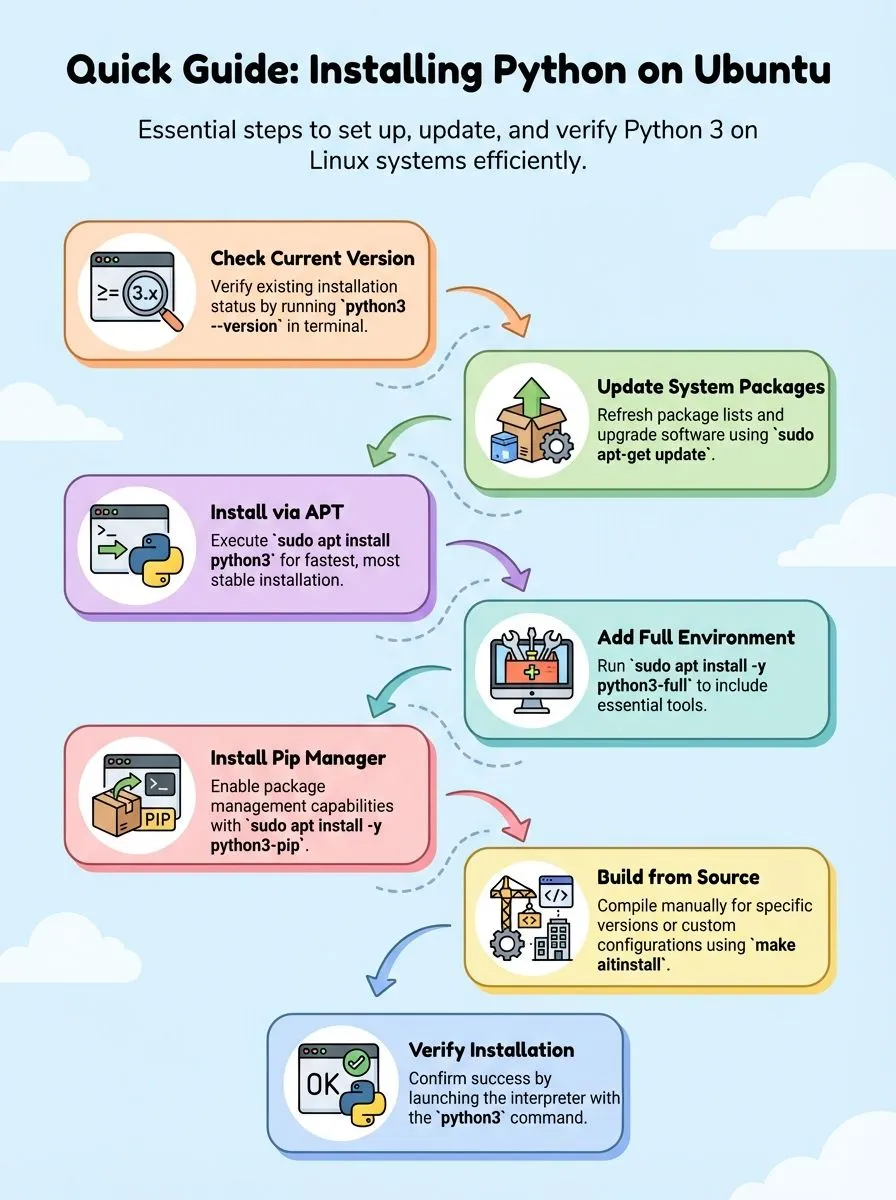
Most Linux users think Python comes ready to use on Ubuntu systems. This belief leads to confusion when they discover their Ubuntu 22.04 or Ubuntu 24.04 installation might lack the latest Python 3.12 version or essential tools like pip.
Learning how to install python in ubuntu properly ensures developers get the right version with all needed components for their projects.
Alex Herrick brings over ten years of web development experience to this guide, having helped countless developers set up their Ubuntu development environments for Python programming.
His expertise in creating custom solutions makes complex installation processes simple and clear. This guide covers everything needed to get Python running perfectly on any Ubuntu system.
Key Takeaways
- Ubuntu systems come with Python 3 pre-installed, but may lack the latest Python 3.12 version or essential tools like pip.
- APT package manager provides the fastest Python installation method using
sudo apt install python3for most Ubuntu projects. - Building Python from source gives complete control and access to specific versions not available in Ubuntu repositories.
- Users can verify successful Python installation by checking version with
python3 --versionand testing pip functionality. - Virtual environments and deadsnakes PPA offer flexibility for managing multiple Python versions across Ubuntu 20.04 to newer releases.
How do I check if Python is already installed on Ubuntu?

Ubuntu systems come with Python 3 pre-installed by default. Checking the current python version helps users understand what tools they already have available.
- Open the linux terminal using Ctrl+Alt+T keyboard shortcut to access the command line interface.
- Type
python3 --versionto check the installed Python 3 version on the ubuntu system. - Run
command -v python3to verify the Python interpreter location at/usr/bin/python3. - Execute
python --versionto see if Python 2 exists, though Python 2 is no longer supported. - Check if pip3 package manager is available by running
command -v pip3in the terminal. - Verify pip installation status using
command -v pipto confirm the python package installer. - Test the default python command by typing
pythonto see which version launches automatically. - Install the
python-is-python3package if users wantpythonto point to Python 3 instead of Python 2.
The next step involves updating system packages before installing any new python versions.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IqETj6wHkfs
How do I update and upgrade system packages on Ubuntu?
After checking your Python installation status, you need to prepare your Ubuntu system for new software installations. Keeping your system packages current ensures smooth Python installation and prevents compatibility issues.
- Open the terminal application on your Ubuntu system to access the command line interface for package management tasks.
- Run
sudo apt-get updateto refresh the package lists from all configured repositories and download the latest package information. - Execute
sudo apt-get upgradeafter updating to install newer versions of all currently installed packages on your system. - Wait for the upgrade process to complete, which may take several minutes depending on the number of packages requiring updates.
- Type your password when prompted, as both update and upgrade commands require administrator privileges to modify system files.
- Review the list of packages that will be upgraded and press ‘Y’ to confirm the installation of updated packages.
- Restart your Ubuntu system after major upgrades to ensure all system changes take effect properly before installing Python.
- Verify the update process completed successfully by checking the terminal output for any error messages or failed installations.
Installing Python with APT package manager
The APT package manager offers the fastest way to install Python on Ubuntu systems, giving developers instant access to Python 3 without complex setup procedures.
How do I install Python using APT on Ubuntu?
APT package manager makes installing Python on Ubuntu simple and fast. This method works great for most python projects and gives users a stable version of python.
- Open the terminal application – Press Ctrl+Alt+T to launch Ubuntu’s command line interface where all installation commands run.
- Update package lists first – Run
sudo apt updateto refresh your system’s software repository and get the latest package information. - Install Python 3 with a single command – Type
sudo apt install python3to download and install the latest version available in Ubuntu’s repository. - Get the complete Python environment – Use
sudo apt install -y python3-fullfor a more complete setup that includes additional tools and libraries. - Add pip package manager – Execute
sudo apt install -y python3-pip python3-pip-whlto install pip, which helps manage Python packages from PyPI. - Install specific Python versions – For Ubuntu 16.10 and newer, run
sudo apt-get install python3.6to get Python 3.6 specifically. - Access your Python interpreter – After installation, find Python at
/usr/bin/python3and start coding right away. - Use pip3 for package management – Pip3 works with Python 3, while pip handles Python 2 packages on Ubuntu systems.
Installing Python from source code
Installing Python from source gives developers complete control over their Python setup and access to the latest features before they reach package managers. This method proves essential when users need specific Python versions or want to customize their installation for unique project requirements.
How do I build and install Python from source on Ubuntu?
Building Python from source lets users install versions not available in Ubuntu repositories. This method gives advanced users complete control over their Python installation.
- Install build-essential and required dependencies – Run
sudo apt install build-essential libssl-dev libffi-dev libncurses5-dev libgdbm-dev libsqlite3-dev libbz2-dev liblzma-dev zlib1g-devto get all needed packages for compilation. - Download the Python source tarball from the official website – Visit python.org and download the specific version needed, then extract the files using
tar -xf Python-X.Y.Z.tgzwhere X.Y.Z represents the version number. - Navigate to the extracted directory and configure the build – Change to the Python source folder and run
./configure --enable-optimizationsto prepare the build with performance improvements enabled. - Compile Python using make command – Execute
make -j$(nproc)to build Python using all available CPU cores, which speeds up the compilation process significantly. - Install the compiled Python interpreter – Run
sudo make altinstallto install Python without replacing the system python, placing the new interpreter in/usr/local/bin/pythonX.Y. - Manually install pip and setuptools for the new Python version – Download get-pip.py and run
/usr/local/bin/pythonX.Y get-pip.pysince source installations do not include pip automatically. - Create symbolic links for easier access – Link the new Python binary to a convenient location or add
/usr/local/binto the PATH environment variable for quick access. - Test the installation with a simple Python command – Run
/usr/local/bin/pythonX.Y --versionto confirm the installation worked correctly and shows the expected version number.
The next step involves checking that Python installed correctly on the Ubuntu system.
How can I verify that Python was installed correctly?
Testing the Python setup ensures everything works properly for future projects. These simple checks confirm the installation was successful and all components function correctly.
- Run the version check command – Type
python3 --versionin the terminal to see the installed Python version number displayed on screen. - Launch the Python interpreter – Execute
python3in the terminal to start the interactive Python prompt where code can be tested directly. - Verify the interpreter location – Check that Python lives at
/usr/bin/python3which links to the default Python 3.x version on the system. - Test pip package manager – Run
python3 -m pip --versionto confirm pip works correctly for installing Python packages and libraries. - Check pip3 command availability – Use
command -v pip3to verify the pip3 command exists and points to the correct location. - Test virtual environment support – Create a test venv using
python3 -m venv test_envto ensure virtual environment functionality works properly. - Verify IDLE availability – Launch IDLE by typing
idle3in the terminal to confirm the Python development environment installed correctly. - Test package installation – Install a simple package like
pip3 install requeststo verify the package management system functions without errors.
Conclusion
Python installation on Ubuntu becomes straightforward with the right approach. Users can choose between APT package manager for quick setup or source compilation for specific versions.
Virtual environments help manage different projects without conflicts. The deadsnakes PPA offers access to multiple Python versions including 3.13. These methods work across Ubuntu versions, from 20.04 to newer releases, giving developers flexibility for their coding projects.
For those using a Mac, check out our guide on how to install Python on macOS.
FAQs
1. How do I install Python on Ubuntu Linux?
Ubuntu comes with Python already installed, but you can install the latest version using APT software. Open your terminal and run “sudo apt update” followed by “sudo apt install python3” to get the newest Python version for your Ubuntu system.
2. What’s the best way to set up a virtual environment for Python development?
Use the venv module to create a virtual environment that keeps your projects separate. Run “python3 -m venv myproject” to create a new environment, then activate it with “source myproject/bin/activate” before installing any dependencies.
3. Can I install multiple Python versions on my Ubuntu 20.04 system?
Yes, you can use pyenv to manage different Python versions or install through the deadsnakes PPA repository. The deadsnakes PPA lets you install newer versions like Python 3.13 alongside your system’s default version.
4. How do I install Python packages using pip on Ubuntu?
First install pip with “sudo apt install python3-pip” if it’s not already available. Then use “pip install numpy” or any other package name to install libraries from the Python Package Index into your environment.
5. What dependencies do I need to install before building Python from source?
Install software-properties-common and build tools first with “sudo apt install build-essential software-properties-common”. This installation guide ensures you have all the necessary components for compiling Python from source code on your Linux distribution.
6. Which development environment works best for Python programming on Ubuntu?
Visual Studio Code offers excellent Python support with debugging tools and extensions. You can also use other integrated development environments, but Visual Studio Code provides great features for both beginners and experienced developers working on Ubuntu using Python.

