Many developers struggle with organizing complex data in Python. A python multi dimensional array acts like a table with rows and columns, making data storage simple and neat. This guide shows how to create, access, and work with these powerful data structures using both lists and NumPy.
Master these skills today.
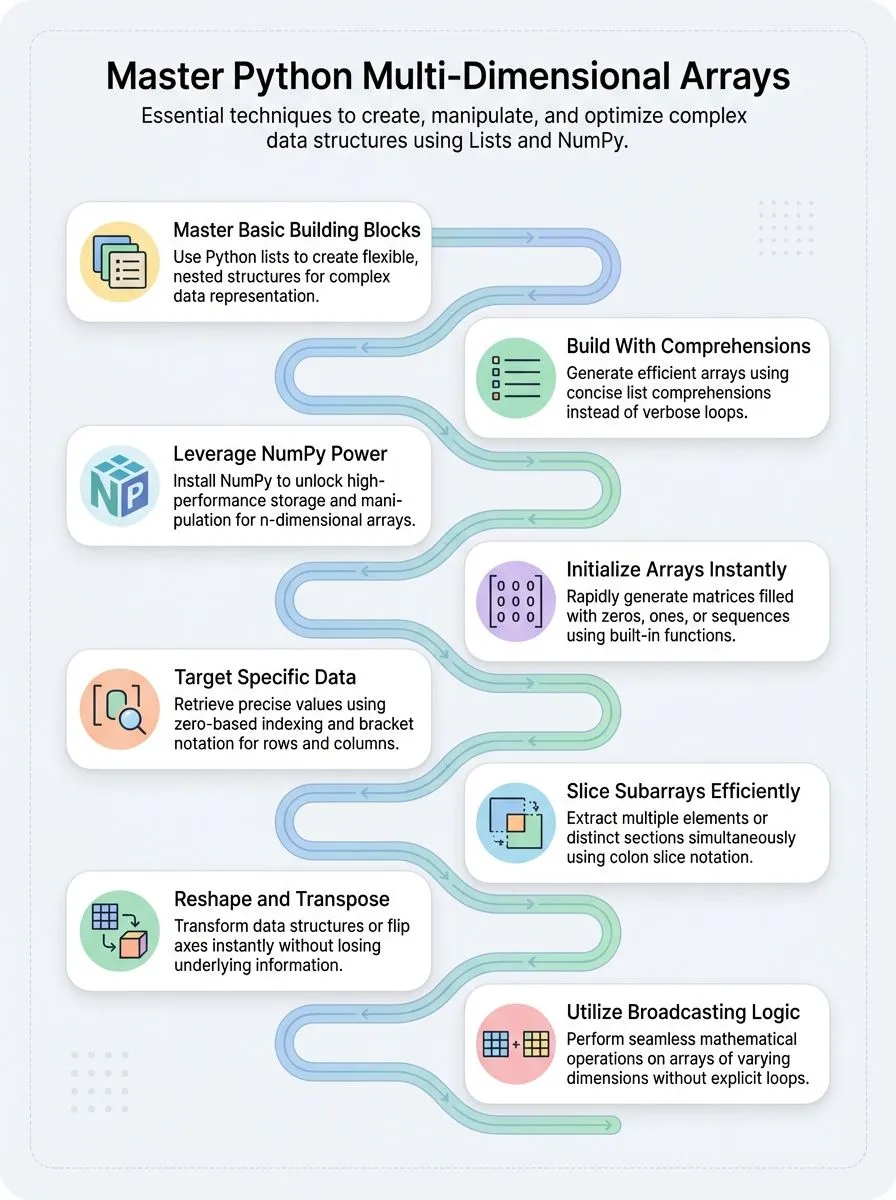
Key Takeaways
- Python multi-dimensional arrays organize complex data using nested lists or NumPy library for efficient storage and manipulation.
- NumPy provides faster array creation methods like zeros(), ones(), and reshape() compared to basic Python list approaches.
- Access array elements using bracket notation with row and column positions, starting from zero-based indexing system.
- Broadcasting allows mathematical operations between arrays of different shapes without writing complex loops or manual reshaping.
- Advanced operations include transposing arrays, applying mathematical functions, and performing element-wise calculations across entire data structures.
What are the basic data types in Python?

Python variables themselves are untyped, but every value assigned to them has a strong type. This flexibility makes Python perfect for creative professionals and tech enthusiasts who want to build powerful applications without getting bogged down in complex syntax.
Python offers several fundamental data types that serve as the foundation for creating more complex structures like multi-dimensional arrays.
Python’s dynamic typing system gives programmers the freedom to focus on solving problems rather than managing memory.
The language provides integers for whole numbers, floats for decimal values, strings for text data, and booleans for true/false logic. Lists stand out as Python’s most versatile data structure, allowing programmers to store multiple elements in a single variable.
These lists become the primary building blocks for creating multi-dimensional arrays, where developers can nest lists inside other lists to represent complex data structures like matrices.
Understanding these basic types helps developers choose the right approach for their specific programming needs, whether they’re working on data science projects or building creative applications.
How to create multi-dimensional arrays in Python
Creating multi-dimensional arrays in Python opens doors to powerful data manipulation and mathematical operations. Python offers multiple approaches to build these array structures, from simple list methods to advanced NumPy library functions that handle complex data efficiently.
How do you create multi-dimensional arrays using lists?
Python lists offer a simple way to build multidimensional arrays without extra libraries. Developers can create complex data structures using nested lists and basic Python syntax.
- Build a 2D array by explicit assignment – Create arrays like
m=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]to store structured data in rows and columns. This method works well for small, fixed-size matrices. - Use nested for loops to initialize arrays – Generate zero matrices with specific dimensions using loops that append elements to each row. This approach gives full control over array creation and initialization.
- Apply list comprehension for efficient creation – Write
Matrix=[[0 for x in range(w)] for y in range(h)]to create arrays with custom dimensions. This method produces clean, readable code in a single line. - Initialize with multiplication operator – Create arrays using
matrix = [[0]*5 for i in range(5)]to build a 5×5 zero matrix quickly. Each row gets created independently to avoid reference issues. - Start with empty matrix structure – Use
matrix = [[]]to build an empty foundation, then append elements as needed. This flexible approach works well for dynamic array building. - Avoid shallow copying mistakes – Never use
matrix = [[0]*5]*5because it creates shared references between rows. Modifying one element affects multiple rows unexpectedly. - Create repetitive value matrices – Build arrays filled with the same value across all positions using nested loops or comprehensions. This technique works great for initialization and placeholder data.
- Access outer and inner list elements – Navigate multidimensional arrays using double indexing like
array[row][column]to manipulate specific elements. The outer list contains rows while inner lists hold column values.
How do you create multi-dimensional arrays using NumPy?
NumPy stands as the go-to module for creating powerful n-dimensional arrays in Python. This library transforms how developers store and manipulate data across multiple dimensions.
- Install NumPy first – Run
pip install numpyin your terminal to access the array creation functions and methods that make multi-dimensional programming simple. - Create zero-filled arrays – Use
numpy.zeros((5,5))to generate a 5×5 matrix filled entirely with zeros, perfect for initializing data structures before adding real values. - Build arrays with sequential numbers – Apply
numpy.arange(25).reshape((5,5))to create a 5×5 matrix containing values from 0 to 24 arranged in rows and columns. - Generate arrays from Python ranges – Execute
numpy.array(range(25)).reshape((5,5))to produce the same 5×5 matrix with values 0 through 24 using familiar Python syntax. - Fill arrays with identical values – Deploy
numpy.array([5]*25).reshape((5,5))to construct a 5×5 matrix where every element equals 5, useful for constant initialization. - Create uninitialized arrays quickly – Use
numpy.empty((5,5))to generate a 5×5 matrix with random memory values, offering the fastest creation method for temporary arrays. - Make arrays filled with ones – Apply
numpy.ones((5,5))to build a 5×5 matrix containing only ones, commonly used for mathematical operations and calculations. - Convert arrays to Python lists – Call
.tolist()method on any NumPy array object to transform it into standard Python lists for compatibility with other functions. - Append data to existing arrays – Use
np.append(mm, [[1, 2]], axis=1)to add new rows or columns to your array object while maintaining the original structure.
How to access and manipulate multi-dimensional arrays
Working with multi-dimensional arrays requires specific techniques to access elements and change their structure. Python offers powerful methods to retrieve data from complex array structures, modify individual elements, and reshape entire arrays to fit different needs.
How do indexing and slicing work in multi-dimensional arrays?
Multi-dimensional arrays use zero-based indexing for accessing elements. Python treats each array in python as a nested structure where users can specify exact positions using bracket notation.
- Access single elements using row and column positions – Use
array[row][column]syntax to get specific values. The codeprint(array[1][0])outputs4from the second row, first column position. - Loop through entire rows using simple iteration – Write
for row in array: print(row)to display each complete row. This method shows all elements in sequence without complex indexing syntax. - Use nested loops for element-by-element access – Create outer loops for rows and inner loops for columns. The pattern
for i in range(len(a)): for j in range(len(a[i])):processes every single element systematically. - Apply slice notation to extract subarrays – Use colons to grab multiple elements at once. Slicing creates a new array from the original array without modifying the source data structure.
- Handle IndexError exceptions for out-of-bounds access – Python raises IndexError when code tries to access non-existent positions. Always check array dimensions before attempting to access elements beyond the valid range.
- Work with tuple keys for dictionary-based matrices – Access dictionary matrices using
matrix[1,2]format. This approach corresponds to mathematical notation and provides cleaner indexing syntax for complex data structures. - Specify negative indices to access elements from the end – Use negative numbers to count backwards from the last position. This technique helps when the exact dimension of the array remains unknown during runtime.
- Perform operations on selected array sections efficiently – Combine indexing with mathematical functions to modify elements in place. Target specific regions without affecting the entire data buffer or memory allocation.
How do you reshape and transpose multi-dimensional arrays?
Reshaping and transposing arrays gives programmers powerful tools to change data structure without losing information. These operations help creative professionals work with images, databases, and mathematical calculations more efficiently.
- Use numpy.arange(25).reshape((5,5)) to create a 5×5 matrix from a flat array using NumPy’s reshape method.
- Apply numpy.array(range(25)).reshape((5,5)) to transform any flat array into a structured matrix format.
- Access the .T attribute on any NumPy array to transpose rows and columns instantly without writing complex code.
- Call the transpose() function on multi-dimensional arrays to flip data along different axes for mathematical operations.
- Generate arrays with numpy.ones((3,5)) and numpy.zeros((3,5)) to create matrices with specific shapes filled with ones or zeros.
- Convert reshaped NumPy arrays back to Python lists using the .tolist() method after completing array operations.
- Reshape arrays efficiently by specifying the number of elements in each dimension as parameters in the reshape function.
- Transpose 2-dimensional arrays to switch from row-major to column-major data organization for different computer science applications.
- Use reshape operations on arrays to prepare data for image processing, database indexing, and 2D computer graphics tasks.
Advanced multi-dimensional array operations
Advanced multi-dimensional array operations open doors to powerful mathematical computations and data manipulation techniques that transform how developers work with complex datasets.
These operations include applying mathematical functions across entire arrays, performing element-wise calculations, and using broadcasting to handle arrays of different shapes seamlessly.
How do you apply mathematical functions on multi-dimensional arrays?
Mathematical functions turn complex array operations into simple tasks. Python offers powerful tools to perform calculations across entire arrays with minimal code.
- NumPy enables direct mathematical operations – Add, subtract, multiply, or divide entire arrays without loops. The library handles element-wise calculations automatically across all dimensions.
- Built-in functions process arrays efficiently – Functions like
sum,mean,max, andminwork directly on multi-dimensional arrays. These methods calculate results across specific axes or entire data structures. - Broadcasting multiplies arrays of different shapes – This feature applies mathematical operations between arrays with compatible dimensions. Small arrays expand to match larger ones during calculations.
- Element-wise multiplication scales array values – Use the asterisk operator (*) to multiply corresponding elements. This method preserves array structure while transforming data values.
- Matrix operations handle complex mathematics – Functions like dot product, matrix multiplication, and linear algebra operations work seamlessly. NumPy provides specialized methods for advanced mathematical computations.
- Universal functions apply to all elements – Mathematical functions like sine, cosine, logarithm, and exponential work across entire arrays. These operations maintain array dimensions while transforming individual values.
- Aggregation functions reduce array dimensions – Operations like sum or mean can collapse specific dimensions. Control which axes to process using the axis parameter in function calls.
- Custom functions map across arrays – Apply user-defined functions to every element using vectorization. This approach maintains performance while enabling complex mathematical transformations.
What is broadcasting and how is it used with arrays?
**Understanding Broadcasting in Array Operations**
Broadcasting represents NumPy’s powerful method for performing operations on arrays with different shapes without creating explicit loops. This feature allows programmers to add, subtract, multiply, or divide arrays of varying dimensions seamlessly.
NumPy automatically expands smaller arrays to match larger ones during mathematical operations. The system handles this expansion internally, making code cleaner and more efficient.
For example, `numpy.ones((5,5))` and `numpy.zeros((5,5))` can be added together due to broadcasting capabilities. This automatic dimension matching eliminates the need for manual array reshaping in most cases.
Element-wise operations become incredibly straightforward with broadcasting rules. NumPy’s array operations automatically expand dimensions as needed when performing mathematical functions on multi-dimensional data structures.
A scalar value can multiply an entire matrix without writing complex loops. The broadcasting mechanism works by stretching arrays along missing dimensions until shapes become compatible.
List-based arrays require list comprehensions to achieve similar effects, but they lack true broadcasting functionality. This makes NumPy arrays superior for mathematical computations involving matrices and complex data manipulation tasks.
Advanced array operations extend far beyond basic broadcasting concepts.
Conclusion
Python arrays open doors to endless creative possibilities for tech enthusiasts and content creators. These powerful data structures transform complex data handling into simple, manageable tasks.
Creative professionals can now build stunning visualizations, process images, and analyze data with confidence. NumPy arrays provide the speed and flexibility needed for professional projects, while basic Python lists offer perfect starting points for beginners.
Master these tools, and watch your coding skills reach new heights in the digital world.
For a deeper understanding of the basic building blocks used in multi-dimensional arrays, explore our comprehensive guide on Python’s primitive data types.
FAQs
1. What makes Python arrays different from other data types?
Python arrays store data in a structured way, unlike basic string or immutable object types. Arrays let you work with multiple values at once, making them perfect for handling large sets of numbers or text data.
2. How do you handle different types of arrays in Python?
Python supports many types of arrays, from simple 1-d array structures to complex matrix formats. You can use built-in methods to create arrays that hold integers, float64 numbers, or even mixed data types.
3. What are the best methods for manipulating arrays efficiently?
Smart array manipulation starts with understanding offset positions and memory paging. Use Python’s built-in functions to avoid low-level operations that might cause overflow errors with your operand values.
4. How do you work with irregularly shaped multi-dimensional arrays?
Irregular arrays need special handling since each second dimension can have different sizes. Python provides flexible methods that adapt to varying array structures without breaking your code.
5. What common problems should you avoid when working with Python arrays?
Watch out for memory issues when working with large arrays stored in computer files. Always check your array bounds to prevent overflow errors, and use proper method calls to keep your data safe.

