**Download Python for Linux: Install Latest Python 3 Version on Your System**
Many Linux users struggle to find the right way to download Python for Linux systems. They often face confusion about which version to get or how to install it properly. Python 3.12 is now the latest stable release, and it brings better performance and new features that make coding easier.
Most Linux distributions come with older Python versions pre-installed, but developers need the newest tools to build modern applications. Getting the latest Python version opens doors to advanced libraries, improved security, and faster code execution.
Alex Herrick has spent over ten years working with web development and knows how important it is to have the right programming tools installed correctly. His experience with custom WordPress themes and responsive designs has shown him that having updated software makes all the difference in project success.
Python installation on Linux might seem tricky at first, but the process becomes simple when you follow the right steps. This guide will show you exactly how to get Python 3 running on your Linux machine.
Let’s get started with your Python setup today.
Key Takeaways
- Python.org provides the official latest Python 3 versions including 3.15, 3.14, 3.13, and 3.12 for Linux systems.
- Ubuntu users can install Python 3.6 with
sudo apt-get install python3.6after running system updates first. - Fedora systems use
sudo dnf install python3command to install the default Python 3 version through terminal. - Users verify correct Python installation by running
python3 --versionandcommand -v pip3in terminal commands. - Virtual environments help avoid conflicts between system Python versions and project-specific Python interpreter requirements on Linux.
Where can I download the latest Python 3 version for Linux?

Python.org serves as the main source for getting the latest Python 3 version on Linux systems. This official website provides source code archives that work across multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and other operating systems.
Users can access Python 3.15 (pre-release), Python 3.14, Python 3.13 (bugfix versions), and Python 3.12, Python 3.11 (security support versions) directly from the site’s download section.
The platform offers CPython as the traditional implementation for most users. Each release comes with complete downloadable release notes and file verification methods. Python releases from version 3.11.0 and later use Sigstore signing for security, while earlier versions rely on OpenPGP verification.
Windows installers starting from Python 3.14.0a1 include an AUTHENTICODE certificate from the Python Software Foundation for extra protection.
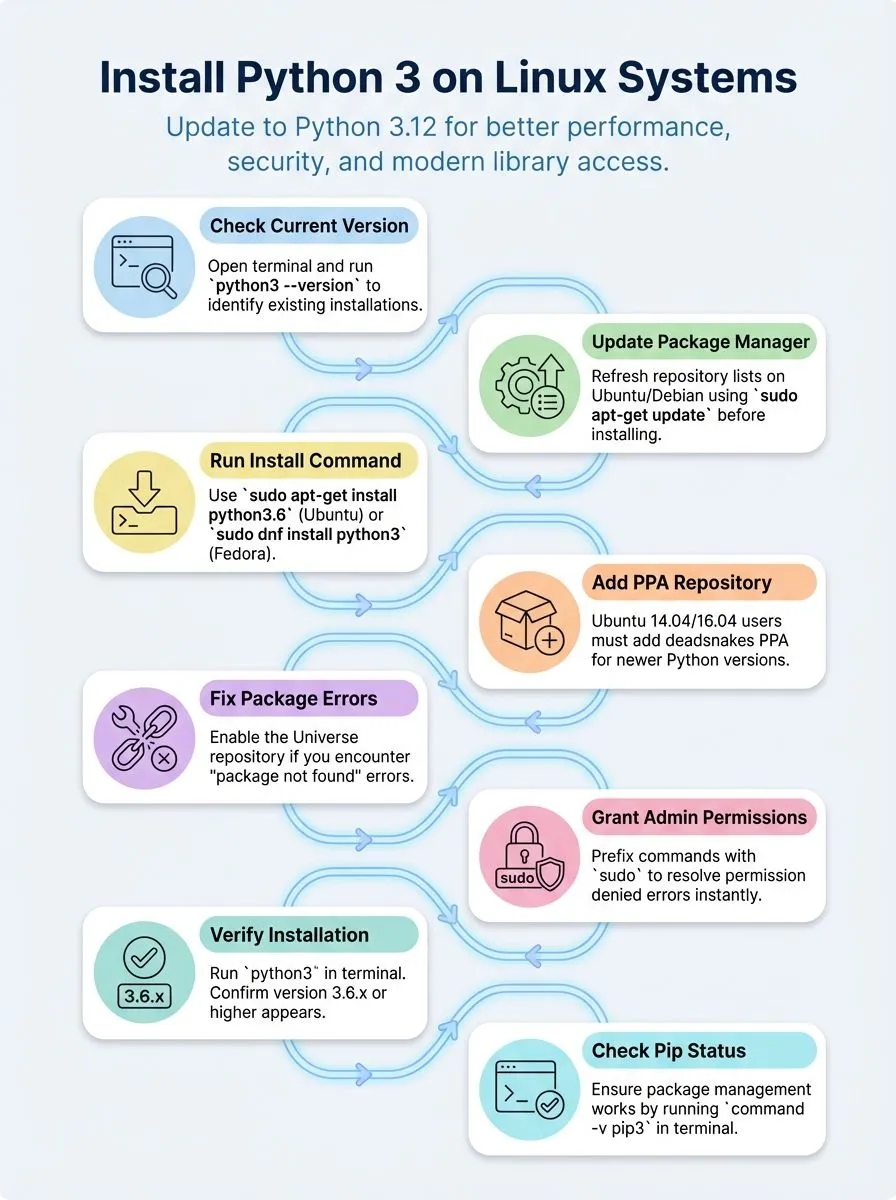
Steps to Install Python 3 on Linux
Installing Python 3 on Linux systems opens doors to powerful programming possibilities, whether users work with Ubuntu, Fedora, or other popular distributions. This process involves multiple methods that cater to different skill levels and system requirements, from using built-in package managers to compiling from source code.
How do I install Python 3 on Linux using the terminal?
Installing Python 3 on Linux systems requires different commands based on your distro. Most modern Linux distributions come with Python pre-installed, but users often need the latest version for their development projects.
- Check your current Python version first – Open terminal and type
python3 --versionto see what version exists on your system already. - Update your package manager before installation – Run
sudo apt-get updateon Ubuntu or Debian systems to refresh the software repository lists. - Install Python 3.6 on Ubuntu 16.10 or newer – Execute
sudo apt-get install python3.6to get this specific version on compatible Ubuntu systems. - Add deadsnakes PPA for older Ubuntu versions – Ubuntu 14.04 or 16.04 users must add this personal package archive before installing newer Python versions.
- Use DNF package manager on Fedora systems – Run
sudo dnf install python3to install the default Python 3 version on Fedora distributions. - Install specific Python versions on Fedora – Type
sudo dnf install python3.9to get Python 3.9 on Fedora 32 systems. - Access Python 3.6 on Ubuntu 17.10 and later – These versions have Python 3.6 as default, accessible through the
python3command in terminal. - Verify pip installation after Python setup – Check for pip with
command -v pip3and install it separately if missing from your system.
What are the common installation issues and how to fix them?
Installing Python 3 through the terminal works smoothly most of the time. Problems can still pop up during the process and slow down your development environment setup.
- Package not found errors occur when the Universe repository stays disabled on Ubuntu systems. Enable it by running
sudo add-apt-repository universebefore attempting the Python installation again. - Python command points to Python 2.7 instead of Python 3 on older Linux distributions. Use
python3command explicitly to run the correct version of Python for your projects. - Missing pip installation happens because some distributions exclude pip by default from their Python packages. Check with
command -v pip3and install pip separately if the command returns nothing. - Outdated package lists cause installation failures when your system tries to fetch old repository information. Run
sudo apt-get updatebefore installing Python to refresh your package database. - Python 3.6 not found on Ubuntu 14.04/16.04 requires adding the deadsnakes PPA for newer Python versions. Execute
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppato access modern Python releases. - Permission denied errors block installations when user accounts lack administrative privileges. Prefix installation commands with
sudoto gain the necessary system access for package management. - Dependency conflicts arise when existing Python packages clash with new installations. Remove conflicting packages first or use virtual environment tools to isolate your Python project dependencies.
- Unsigned executable warnings appear because third-party packages like pip lack official signatures from package maintainers. These warnings are normal and safe to ignore during standard installations.
How can I verify that Python is correctly installed on Linux?
After installing Python on your Linux system, users need to confirm everything works properly. The terminal provides several commands to check the installed Python version. Users can run `python –version`, `python2 –version`, and `python3 –version` to see which versions exist on their system.
These commands show the exact version numbers, helping users identify what they have installed.
On Ubuntu 17.10 and later versions, Python 3.6 comes as the default installation. Running `python3` should display version 3.6.x or higher on these systems. Users working with virtual environments managed by Pipenv can activate their environment with `pipenv shell` and then verify Python by running `python –version` inside the shell.
Virtual environments help avoid confusion between system and project-specific Python versions, ensuring correct interpreter usage. To confirm pip is installed, users can type `command -v pip` or `command -v pip3` in the terminal.
These commands will show the path to pip if it exists on the system.
Virtual environments help avoid confusion between system and project-specific Python versions, ensuring correct interpreter usage.
Conclusion
Python installation on Linux opens doors to countless creative projects. Users gain access to powerful tools for web development, machine learning, and automation scripts. The programming language works seamlessly across Ubuntu, Mint, Fedora, and other distributions through simple terminal commands.
Creative professionals can start building web applications with Django or Flask frameworks immediately after installation. Data scientists benefit from Python’s extensive library ecosystem for analyzing complex datasets.
The open-source nature of both Python and Linux creates the perfect environment for innovation and experimentation.
FAQs
1. How do I download Python for Linux systems like Ubuntu and Linux Mint?
You can install Python on Ubuntu using the APT software manager through the command line. Most Linux distributions, including Ubuntu Linux and Linux Mint, come with Python already installed.
2. What is the latest Python 3 version available for installation?
Python 3.10.12 is one of the recent stable releases available for download. You can check for the newest version on the official Python website or through your Linux operating system’s repositories.
3. Can I install multiple Python versions on my Ubuntu system?
Yes, you can use pyenv to manage different Python versions on your system. The deadsnakes PPA also lets you install another version alongside your current Python installation.
4. How do I set up a virtual environment for Python programming?
Install pipenv or use the built-in venv module to create isolated environments. You can activate the virtual environment using the command prompt, which helps separate your projects and their dependencies.
5. What makes Python useful for software developers and data scientists?
Python is a cross-platform, general-purpose programming language with excellent code readability. It supports web development frameworks like Django and Flask, machine learning algorithms, and artificial intelligence applications, making it perfect for automating tasks and building web applications.
6. Do I need special tools for Python development on Linux?
You can write Python scripts using any text editor, but an integrated development environment like PyCharm makes coding easier. Python works great on Windows, macOS, and Linux platforms, and you can access it through the desktop or command line interface.

